-
![]() ESG in bankingESG-conscious banking should create new and future-proof value streams to build a sustainable and resilient business.Read More
ESG in bankingESG-conscious banking should create new and future-proof value streams to build a sustainable and resilient business.Read More -
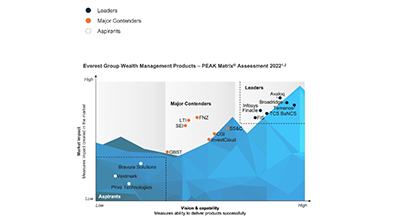
![Everest Group PEAK Matri Everest Group PEAK Matri]() Everest Group PEAK MatrixA comprehensive solution delivering a full spectrum of wealth products as great experiences. It also improves the productivity of financial advisors and streamlRead More
Everest Group PEAK MatrixA comprehensive solution delivering a full spectrum of wealth products as great experiences. It also improves the productivity of financial advisors and streamlRead More -
![]() Subsidiary of an American Bank in IndonesiaFind out how a leading American bank adapts to a digitalized trade and supply chain finance operations as a part of its larger transformation by leveraging Finacle Trade Finance Solution Suite.Read More
Subsidiary of an American Bank in IndonesiaFind out how a leading American bank adapts to a digitalized trade and supply chain finance operations as a part of its larger transformation by leveraging Finacle Trade Finance Solution Suite.Read More
-
![]() Recomposing Banking: Leading the Digital ContinuumReport gives you a glimpse of the major areas where recomposing banking will create significant impact and value, Infosys Finacle has put together a report on..Read More
Recomposing Banking: Leading the Digital ContinuumReport gives you a glimpse of the major areas where recomposing banking will create significant impact and value, Infosys Finacle has put together a report on..Read More -
![]() Core Banking on Cloud: Navigating to the Fast LaneTake a deep dive into cloud-based core banking and explore the imperatives, opportunities and challenges, and the hallmarks of a robust solution.Read More
Core Banking on Cloud: Navigating to the Fast LaneTake a deep dive into cloud-based core banking and explore the imperatives, opportunities and challenges, and the hallmarks of a robust solution.Read More -
![]() Embracing Payments ComposabilityA step-by-step guide for maximizing Real Time Payment opportunities by embracing Payments Composability...Read More
Embracing Payments ComposabilityA step-by-step guide for maximizing Real Time Payment opportunities by embracing Payments Composability...Read More
-
![]() Shaping Banking’s Next: Banking Technology Trends for 2025 and BeyondThe banking industry has been balancing disruption and opportunity for several years now, and the pace of change shows no signs of slowing as we move into 2025 and beyond.Read More
Shaping Banking’s Next: Banking Technology Trends for 2025 and BeyondThe banking industry has been balancing disruption and opportunity for several years now, and the pace of change shows no signs of slowing as we move into 2025 and beyond.Read More -
![]() Virtual Accounts 2.0: Surpass Conventional Cash Management and Unlock Next-Gen PossibilitiesVirtual Account Management was a groundbreaking shift in the banking landscape, revolutionising use cases like cash concentration, pooling, centralised treasury management, and in-house banking (POBO, ROBO, COBO)Read More
Virtual Accounts 2.0: Surpass Conventional Cash Management and Unlock Next-Gen PossibilitiesVirtual Account Management was a groundbreaking shift in the banking landscape, revolutionising use cases like cash concentration, pooling, centralised treasury management, and in-house banking (POBO, ROBO, COBO)Read More -
![]() Unlocking Hybrid CloudAs banks push forward with their digital transformation agenda, cloud serves as a pivotal enabler. Each bank, at varying stages of adoption, crafts its unique path, dictated by context, regulations, and risk appetite.Read More
Unlocking Hybrid CloudAs banks push forward with their digital transformation agenda, cloud serves as a pivotal enabler. Each bank, at varying stages of adoption, crafts its unique path, dictated by context, regulations, and risk appetite.Read More
-
![]() Banking on CloudThis report from Infosys Finacle delves into the need for accelerating cloud adoption, highlights the current state of the industry, and puts forth key recommenRead More
Banking on CloudThis report from Infosys Finacle delves into the need for accelerating cloud adoption, highlights the current state of the industry, and puts forth key recommenRead More -
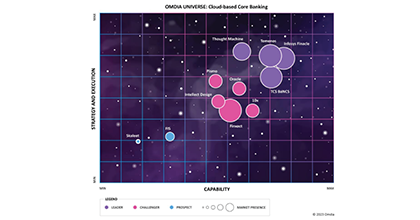
![]() Omdia Universe | Cloud-based Core BankingIn the report, Omdia highlights the following key capabilities of leading cloud-based core banking providers:Read more
Omdia Universe | Cloud-based Core BankingIn the report, Omdia highlights the following key capabilities of leading cloud-based core banking providers:Read more
-
![]() Emirates NBDEmirates NBD consolidates its operations on a single version for scalability, agility, and standardization.Read More
Emirates NBDEmirates NBD consolidates its operations on a single version for scalability, agility, and standardization.Read More -
![]() A Global Top 5 BankDiscover how a global top 5 bank headquartered in the US accelerated payments transformation.Read More
A Global Top 5 BankDiscover how a global top 5 bank headquartered in the US accelerated payments transformation.Read More -
![]() Union Bank of IndiaUnion Bank of India launches Union Virtual Connect (UVConn) by leveraging WhatsApp to provide customers personalized banking services.Read More
Union Bank of IndiaUnion Bank of India launches Union Virtual Connect (UVConn) by leveraging WhatsApp to provide customers personalized banking services.Read More

Esg in Indian Banking Sector: An Equation of Growing Importance
Blogs
Man-made climate change is the most pressing concern of our times. To tackle this challenge, governments and regulatory bodies across the world are driving an ESG transformation of the business world with great urgency. The Paris Climate Agreement, signed in 2015 and legally binding 196 countries to undertake actions to curtail climate change, was one of the most definitive steps in this direction.
As financial custodians of global economies, banks are under significant pressure to play their part. There are two primary areas of ESG impact that banks across the globe can easily and immediately address. First, implementing ESG standards and goals in the bank’s standards. Second, how the bank reflects its ESG consciousness in its policies, especially around lending and illuminating borrowers to be more ESG-focused. Additionally, customer and investor awareness in choosing companies, including banks, that align to sustainability principles is steadily growing.
Regulatory bodies are also drafting guidelines and regulations that compel banking and financial institutions to consider ESG in their risk management framework. It is no longer just about sustainability as an ethical obligation, but as a business and investment driver as well. The good news is, it’s not all gloom and doom for banks. A report by Alvarez and Marsal indicates that leading banks in Europe and North America can boost their revenues by 10% by 2030, with adequate commitment to transitioning to a sustainable economy. These revenues could come from green and sustainable lending products and services in their lending framework.
Banks have the potential to access various revenue streams driven by ESG principles. These could involve assessing and rating clients based on their ESG performance, to ascertain their eligibility for green finance and incentives. Additionally, banks could facilitate connections between clients who produce carbon and those who offset it to promote carbon neutrality. Another possibility is the creation of new products, such as carbon calculators, integrated emission statements, and carbon offset deposits, to enable clients to measure, monitor, and tackle their emissions.
The global Sustainable Development Report places India at 121 (out of 163 countries) in achieving sustainable development goals. While this ranking may not be heartening, India has been increasing focus on ESG. The Indian government has been actively encouraging companies to adopt ESG practices through initiatives such as the Sustainable Development Goals, in conjunction with the UN and the National Action Plan for Climate Change, launched in 2008.
The Indian government has also firmly committed to the 2070 Net Zero goals. In addition, there has been a growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. In 2014, India became the first country to make CSR mandatory, making companies with a certain turnover and profitability to invest 2 percent of their average net profit of 3 years in areas such as education, poverty, gender equality, and hunger. India’s Green Hydrogen mission is expected to be the world’s largest such initiative and is expected help India reach its net zero carbon emission goal by 2070.
For the Indian banking sector, the ESG transition is being largely driven by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). In its report on ‘Climate Risk and Sustainable Finance’, the RBI issued guidelines or suggestions for banks to assess and manage their ESG risks and ensure that their operations and strategies are in line with ESG principles. Banks must leverage this to identify and assess their ESG risks and set targets to reduce them.
The Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) committed to crafting an ESG framework while carrying out credit assessment and including climate risk as part of their risk assessment strategy. Prior to the G20 summit in December 2022, the IBA also brought together a group of banks to address ESG issues ranging from sustainability to green financing. According to a report, 79 percent of the top 100 companies in India publish a standalone ESG report.
Despite the increasing focus on ESG, the Indian banking sector is yet to make a significant impact in the implementation of ESG policies. According to the CRISIL Sustainability Yearbook 2022, a majority of the financial institutions in India were not tracking their own Scope 3 emissions. Moreover, banks and financial institutions are yet to align to the BSBR and Net Zero commitments.
Several shortcomings in ESG reporting and tracking can be attributed to the lack of awareness and understanding of the importance of ESG among banks, as well as a lack of incentives and stringent regulations to adopt ESG practices. Yet, banks are increasingly being asked to rise to the challenge. According to a report by MSCI, banks and financial institutions will be expected to conduct climate-risk stress tests.
Banks are discovering that pursuing both ESG and digital transformation can have a mutually reinforcing effect, driving progress in both areas simultaneously. Although the challenge of undertaking both digital and ESG transformations may appear formidable, banks can find reassurance in the fact that there are substantial areas of overlap between the two agendas. Moreover, banks that can achieve a reasonable degree of maturity in both areas will have a distinct competitive advantage in the market, with few rivals capable of matching their comprehensive offerings. The successful implementation of dual transformation would require banks to not only modernize their technology systems and business practices, but also to affect a shift in their workforce, culture, organizational structure, and in certain cases, their fundamental values.
In the EU, several countries have begun implementing ESG laws and other nations are following in their footsteps. This heralds a new age of banking where banks will be held accountable for their own ESG impact and be expected to monitor the ESG preparedness of their customers.
This article was previously published in the Financial Express.


©2025 -Edgeverve Systems Limited | All rights reserved